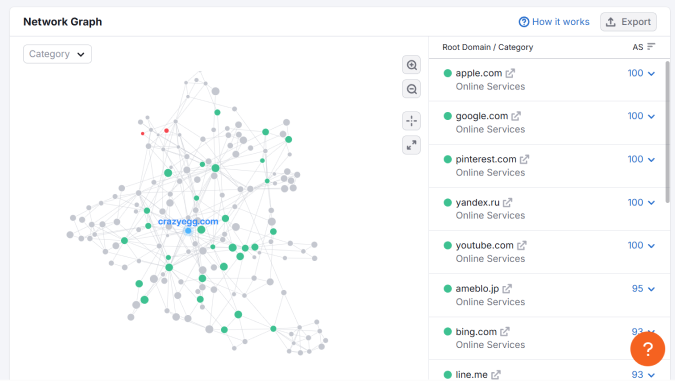
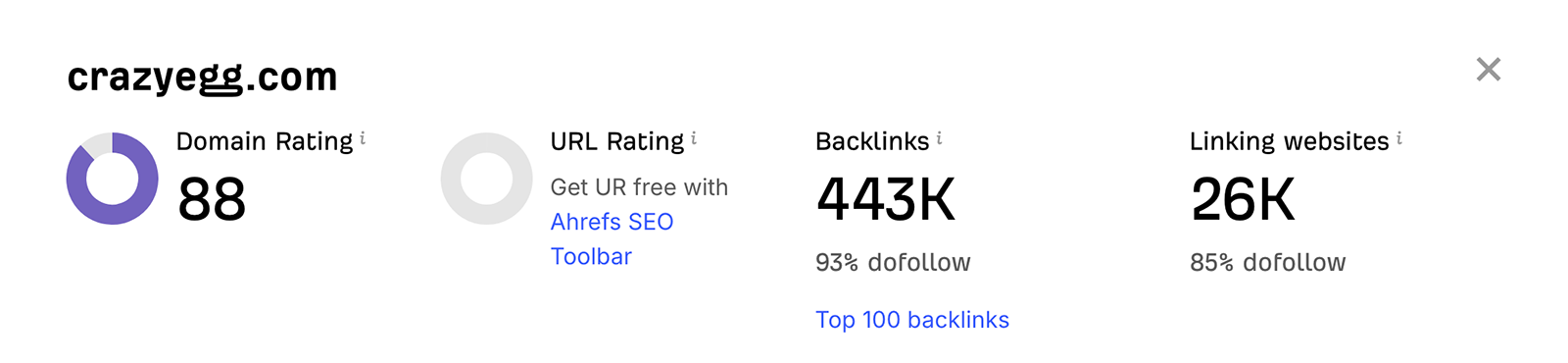
When SEOs talk about “link juice,” it might sound like a throwback to the early days of PageRank and keyword stuffing.
But the core idea behind it still holds weight today.
The concept of passing value through links remains central to how search engines understand and rank content. In this post, we’ll unpack how link juice works and whether it still matters for SEO in the age of AI.
What is Link Juice?
Link juice describes the authority or value passed from one webpage to another through hyperlinks. It originated as a slang term among the SEO community in the 2000s to align with how Google’s PageRank algorithm used links in its ranking algorithm.
It’s the idea that when a page with strong SEO signals links to another page, some of that authority is transferred, helping the linked page rank higher in search results.
This value can come from both external backlinks and internal links within the same website.
While the more formal term link equity is often used today, “link juice” remains a useful shorthand for understanding how ranking power flows through the web.

What Factors Affect How Much Link Juice Is Passed?
Not all links are created equal. The amount of link juice passed from one page to another depends on a variety of factors, from where the link is placed, to the relevance of the content it connects.
These signals help search engines (and increasingly, AI systems) determine how much trust or authority should be transferred through each link.
Authority of the Linking Page
The higher the authority of the page doing the linking, the more link juice it can pass.
This is why backlinks from well-known, trusted websites carry significantly more weight than links from low-authority or spammy sites.
A page’s overall trustworthiness and domain strength are evaluated when deciding how much equity to assign to its outbound links. If your content is referenced by a page that already ranks well and earns traffic, it’s a strong signal that your page might be worth ranking too, especially if other trusted sources also point to it.
Placement of the Link on the Page
Links placed higher on a page, especially within the main body content, tend to pass more link juice.
Search engines consider these more important than links buried in footers, sidebars, or boilerplate sections.
For example, an editorial link in the first few paragraphs of a blog post carries more weight than a tiny link buried in a footer.
This idea isn’t new. Even older versions of Google’s algorithms paid attention to where links appeared on a page and which parts of the content mattered most to readers.
Distribution of Authority
Not every link passes SEO value. For a link to transfer link juice (or authority), it needs to be what’s called a “follow” link.
This simply means it’s a normal hyperlink without any special instructions telling search engines to ignore it.
Only follow links pass link juice. If a link is marked as “nofollow,” it tells search engines not to transfer authority to the target page.
Other modern attributes (like rel=”sponsored” for paid links or rel=”ugc” for user-generated content) further clarify the relationship and often restrict link equity from being passed. Similarly, if a link is hidden behind JavaScript or blocked from crawling, it may not be counted at all.
These distinctions are more than technical quirks. They’re part of how search engines prevent manipulation and protect the integrity of their ranking systems.
Link Relevance
Relevance between the source and target content has become a key factor in how much link juice is passed.
Search engines (and now LLMs) evaluate whether two pages are topically related. The more aligned the themes, the more value is transferred.
This is no longer a fuzzy guess. Thanks to advances in natural language processing, algorithms can now compare embeddings of passages and calculate semantic similarity using techniques like cosine similarity.
That means a link from a page deeply relevant to your topic isn’t just a trust signal, it’s also a signal that helps define what your page is about.
Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable words used in a hyperlink. It acts like a label for the link and can be used as a clue for what topic relates to the link.
It helps search engines understand what the linked page is about and which keywords it should rank for. While it doesn’t affect the amount of link juice passed, it does influence how that juice is interpreted.
For example, a link with the anchor text “best contract lawyer” sends a clearer topic signal than one that simply says “click here.” Strategic use of anchor text can help build topical authority, but over-optimizing with keyword-stuffed anchors can look unnatural and potentially backfire.
Number of Links on the Page
Link juice is divided across all the links on a page. Think of it how a birthday cake gets sliced thinner the more people show up to the party.
If a page links to only a handful of external pages, each one receives a larger share of equity.
But if there are dozens of outbound links, each link passes significantly less value. While this doesn’t mean you should hoard links or avoid linking out entirely, it’s a reminder that outbound links dilute authority and that thoughtful linking can shape how juice flows throughout your site and beyond.
Does Link Juice Still Matter?
Yes, the core idea of link juice still matters, but not in the way it once did.
To understand why, it helps to look back at how Google originally measured a page’s importance. In its early days, Google relied on a system called PageRank. This was an algorithm that treated links like votes in a popularity contest. Each link pointing to a page was considered a vote of confidence, and the more (and higher-quality) votes a page had, the more important it was deemed.
SEOs tried to game this by sculpting PageRank. They used tactics like hoarding internal links or adding nofollow tags to control where link juice flowed. This tactic no longer works today, mainly because Google’s algorithms have become much more sophisticated and evolved beyond PageRank.
However, links remain one of the most trusted signals for assessing authority, credibility, and context online.
In fact, Google’s own documentation still cites backlinks as a key part of how it evaluates trustworthy content. LLMs, like ChatGPT, also use authoritative websites (with many quality links) in their training data.
So the core idea that links still transfer value from one site to another still matters.
What’s changed is how search engines interpret the value that gets passed. It’s not just about quantity or simple authority. With the power of LLMs and semantic processes, search engine algorithms also look at context, relevance, and how naturally the link appears in content.
And in an AI-driven search landscape, where LLMs synthesize answers across multiple sources, links continue to influence which pages are crawled, cited, and surfaced in generated responses.
So, no, it’s not the wild west of PageRank sculpting anymore, but yes, links still deliver value. They just need to be earned and managed more thoughtfully.
How to Maximize Link Equity in Modern Search
Today’s link equity strategies go beyond just building backlinks. This is because even unlinked brand mentions now have intrinsic value in a way they did not in the past.
With modern search engines and AI systems assessing everything from page context, brand sentiment and topical relevance, it is more important than ever to take a thoughtful, structured approach to how authority flows into and throughout your site.
Here are six high-impact ways to make the most of your link juice today.
1. Earn Links and Mentions From Authoritative, Relevant Sources
Not all backlinks are equal. Links and mentions from high-authority domains that are topically relevant to your content will pass far more value than unrelated or low-quality links.
Relevance plays an even bigger role now that Google and AI systems evaluate the semantic relationship between pages. When a reputable site in your niche links to you, it not only boosts rankings but also reinforces your authority on that specific subject.
Skip link schemes and mass outreach. Instead, focus on earning links and mentions naturally through original research, expert commentary, or standout content that fills a real gap in your industry.
2. Use Smart Internal Linking to Distribute Authority
Internal links are your secret weapon for directing link equity to important pages. They help search engines understand your site’s structure, prioritize your most valuable content, and establish topical relationships between pages.
For example, linking from a high-performing blog post to a new service page can give that service page a visibility boost. Use keyword-rich (but natural) anchor text, and be intentional about which pages get linked from key hubs.
This tactic is especially important for new or underperforming pages that haven’t yet earned external links, internal linking can help them surface sooner.
3. Fix Broken Links and Redirect Old URLs
Broken pages waste valuable link equity.
If you’ve deleted or changed URLs without proper redirects, any backlinks pointing to those pages are essentially dead ends and the authority they once carried is lost.

Use tools like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog to identify broken inbound links, then implement 301 redirects to relevant, live pages. This not only recaptures lost value but also improves the user experience and keeps your site’s authority intact.
It’s one of the easiest, highest-ROI technical SEO tasks you can do, especially for older or frequently updated websites.
4. Avoid Excessive Outbound Links on Key Pages
Link equity is finite, and the more outbound links you include on a page, the less authority each one can pass.
This doesn’t mean you should never link out. In fact, linking to reputable sources can be a positive signal.
But be strategic. Avoid linking to too many unrelated domains, affiliate-heavy sites, or low-value resources, especially from pages that already carry strong SEO weight.
Think of it like dividing up a cake: the more slices you serve, the smaller each one gets. Save the biggest slices for links to pages that matter most.
5. Make Content Link-Worthy for AI-Generated Results
With AI-powered search (like Google’s AI Overviews, AI Mode or even ChatGPT) now summarizing answers across multiple sources, your content needs to be citation-worthy, not just keyword-optimized.
That means publishing content that’s accurate, insightful, and written with subject-matter depth. This is the kind of material LLMs are more likely to quote, paraphrase, or reference in responses.
Add original insights, stats, or expert takes that others will want to cite.
If your page becomes the go-to resource in your niche, it’s more likely to earn valuable links and surface in generative answers, giving your site an edge in both SEO and AI visibility.
6. Build Topical Authority With Interlinked Content Hubs
Topical authority plays a bigger role than ever in how search engines evaluate your site, and link equity helps reinforce it.
Create interlinked content hubs around specific themes or categories. For example, instead of publishing five unrelated blog posts about SEO, create a well-structured cluster that links to a central pillar page.
This helps search engines understand your depth on a subject and pass equity throughout the cluster, rather than isolating it to a single article.
The result: stronger visibility across all related terms and a more coherent experience for both search engines and users.
Link juice might be an old-school term, but the core idea of it still matters. Links between pages share value and authority.
As search evolves, the smartest strategies aren’t about gaming the system; they’re about structuring your content and links in ways that make sense to both humans and machines. When you do that well, the results compound over time.