Search is no longer just about matching the exact words you type.
Modern search engines aim to understand what you mean, not just what you say. That shift is thanks to something called semantic search.
It’s what helps Google, ChatGPT, and even basic site search tools deliver more relevant, meaningful results.
In this guide, we’ll break down what semantic search is and why it matters—no jargon, no coding, just plain English.
What Does “Semantic” Mean?
The word semantic is all about meaning. More specifically, semantics is the field most concerned with how machines understand the meaning of words we use and how these words relate to each other.

It’s easy to personify machines and think they understand words like we do. But they don’t.
Humans can easily understand that the words cat, car, and cap are unrelated. But a lot needs to happen for a machine to develop that same understanding. Until then, all three of these words are strings of characters that begin in the exact same way.
This is a really important distinction for search engines to be able to make because it’s how they’re able to show results that make more sense to humans.
What is Semantic Search?
Semantic search is a method of retrieving documents and information that is not based on matching the exact words a searcher used in their query.
Rather, it is about understanding the searcher’s intent and meaning behind what they’re looking for and either providing the answer they’re seeking directly or getting them one step closer to the ideal solution.
For example, if you search for something like “5cm to inches” what’s more helpful?
Results like this, that try to match the words in your query to available webpages:
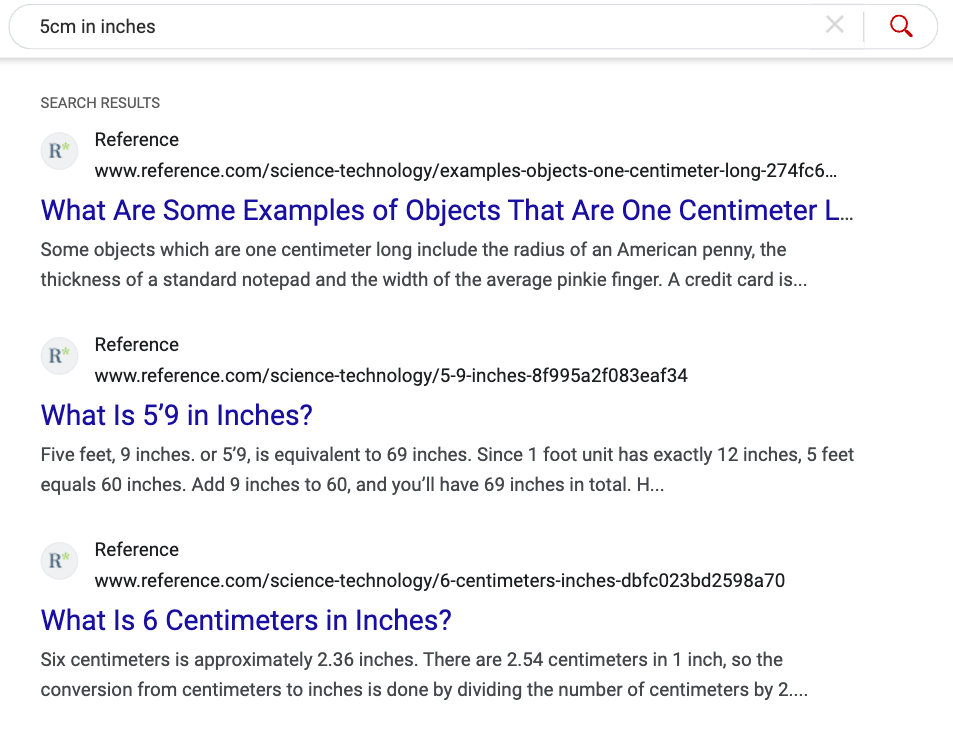
Or results like this that adapt their design based on the inferred meaning of the query (to do a calculation)?

To be clear, the calculator Google adds to search results does not make it semantic.
Instead, the algorithm’s ability to understand that the intent behind the query is to perform a calculation is what’s semantic. It understands the meaning of the query and shows more relevant results.
Semantic Search vs Traditional Search
For a long time, most search engines worked by matching the exact words you searched for to documents they found on the internet. It’s a bit like how Google Scholar works today:

This method of retrieving information or documents is called “lexical search” because it relies on the exact words used and will only show documents that mention those words.
Semantic search, on the other hand, is more liberal with how it matches what a user looks for with the documents it can return. It tries to understand the meaning behind the words searched.
For example, Google Scholar returned a bunch of articles about the exact condition known as “liver disease”. But the top-ranking article on Google (also the top-cited article in the AI Overviews section) is about “liver problems” more generally:

The results also mention and highlight connected conditions like cirrhosis and liver failure.
In the case of cirrhosis, there’s no “lexical” (or word-based) similarity to “liver disease” which is why old school search engines would not typically display results about it.
But there is a meaning-based connection. Cirrhosis is a closely connected concept to liver disease and that’s why modern search engines that take a semantic approach can show information about it.
How Semantic Search Works (In Plain English)
So, in a nutshell, semantic search works by figuring out what you mean and then finding the most relevant results based on that meaning, not just the words you typed.
But it sounds a lot simpler than it actually is.
Modern search systems rely on a mix of techniques that help them interpret language more like a human would. Here are a few key ingredients that make it work:
1. Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing is a field in computer science that teaches machines to read, interpret, and generate human language.
It’s been around since the 1950s, and it now sits under the umbrella of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Some major tasks that NLP can help with are:
- Speech recognition
- Text classification
- Understanding natural language
- Generating natural language
It’s very relevant to the topic of semantic search since all of the above functions of NLP are a core aspect of how modern search works.
NLP helps a search engine break down your question into smaller parts, understand sentence structure, and recognize things like synonyms and common phrases.
It’s how the system knows that “how to fix a sore back” and “lower back pain remedies” are asking for the same thing.
2. Search Intent
Before presenting you with results, semantic search engines try to understand the why behind your query.
Think of it as the difference between searching for “apple” because you want fruit vs. because you’re looking for the company. Or, like the “inches to centimeters” example above, understanding that you want to make a calculation.
This intent understanding helps the search engine tailor results that answer your question, even if your words were vague or can have multiple meanings.
3. Embeddings
Some search engines convert words, phrases, and even entire documents into embeddings, which are like coordinates in a big map of meaning.
Imagine every word or idea is a dot on a giant map, where similar ideas are closer together. That’s what embeddings are.
Search engines and LLMs can embed the topics in your search query as well as the documents they think are related. Then, they’ll show you the results based on what’s mapped closest to your query.
This allows the search engine to find meaning-based matches, even when the exact words don’t match.
4. Vector search
Once everything is placed on that “meaning map,” the search engine uses vector search to find the closest match. Think back to high school math—vectors are lines on a graph. So, vector search is about using the lines connecting to embeddings to see how near or far they are from each other.
This is where a bunch of math and calculations happen that aim to answer the question, “Which other dots are closest to the one just added?”
This means you might search for “heartburn medicine,” and get results about “antacids” or “acid reflux relief,” even if those words weren’t in your original query.
A popular example used in the coding community to explain this is how machines do word math like “King – Man + Woman = Queen”

(Source)
The vectors allow a machine to see that king is to man what queen is to woman.
Yes, it seems strange and counterintuitive, and it’s not at all how humans think… which is the point. Computers cannot think like humans. They can simulate it, but they can’t actually do it, hence all the math.
5. Machine learning models
Over time, semantic search improves by learning what kinds of results people find helpful—and which ones they ignore.
This learning process helps it make smarter predictions about what users are really looking for, even when the queries are messy, misspelled, or unusual.
It helps to think of the machines behind the scenes learning in a similar way to how children do.
They get exposed to a bunch of data and then try to make sense of it by categorizing and grouping similar things together. However, unlike children, machines will ‘make sense’ of it by creating vectors and running calculations (as mentioned earlier).
They do this in order to find the highest probability of things that belong together.
The more times two words get mentioned together, the higher the chances they are connected. The more that people use a specific sequence of characters, the more likely it’s a word that has meaning to humans, unlike a random sequence of characters like “svxc”, which means nothing to us.
6. Personalization and context
Sometimes, semantic search takes into account what you’ve searched before, your location, or other signals to predict what you’re likely looking for now. In the case of LLMs, they can also remember your past conversations.
They embed these. That’s how they “remember” you like a particular type of result or output, so once it learns that pattern about you, an LLM modifies its responses to give you what it thinks you want.
This kind of contextual relevance also helps refine search results on platforms like Google so that each user feels like they get exactly what they wanted.
How Semantics Are Used by Different Search Engines and LLMs
Semantics are used in search in many different ways. Every search engine and LLM has it’s own algorithms and models that are intricately designed by their engineering teams.
For example, the search engine Baidu uses two types of indexes (a lexical one and a semantic one) from which it pulls search results. It’s a hybrid approach that allows users to benefit from exact match keyword searches.
Think of the last time you were searching for a song and entered a partial lyric you remembered. That type of search requires the old school lexical matching approach for it to return what you’re looking for (ie, the rest of the song).
Google also uses a hybrid approach. For a long time, it has been using vectorization and also interweaving semantics during the reranking phase (the step right before it shows results to a user).
But things are rapidly changing in this space thanks to LLMs.
LLMs skew towards being almost completely semantic in nature, and as search engines add more LLM-based features (like Google’s AI Overviews and AI mode), it’s a real possibility that they could become even more semantic in the future.